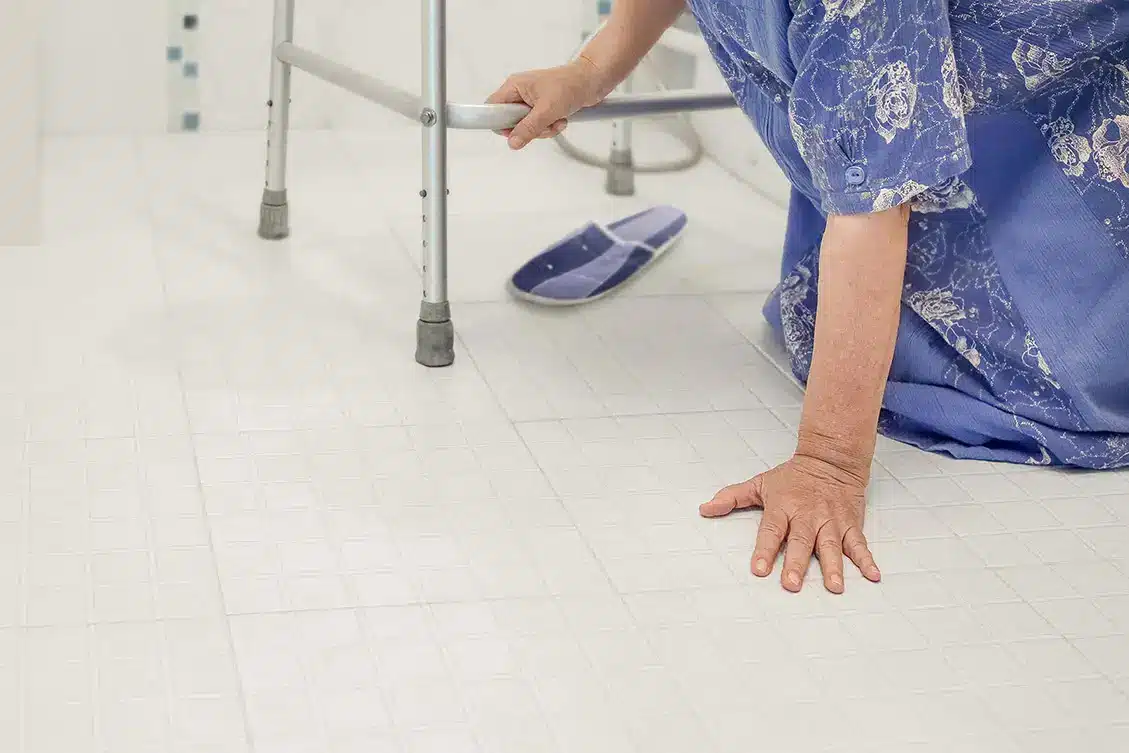
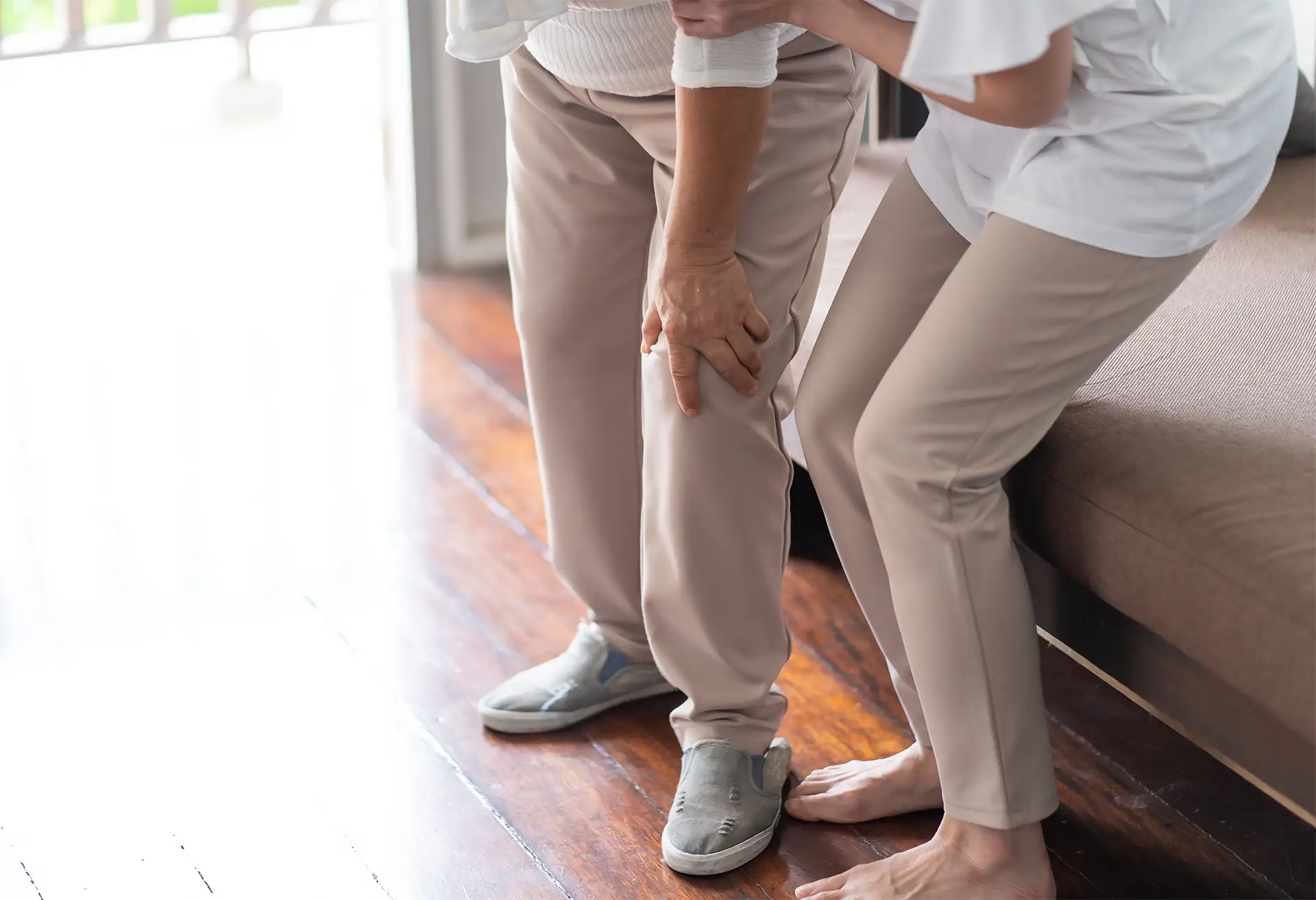
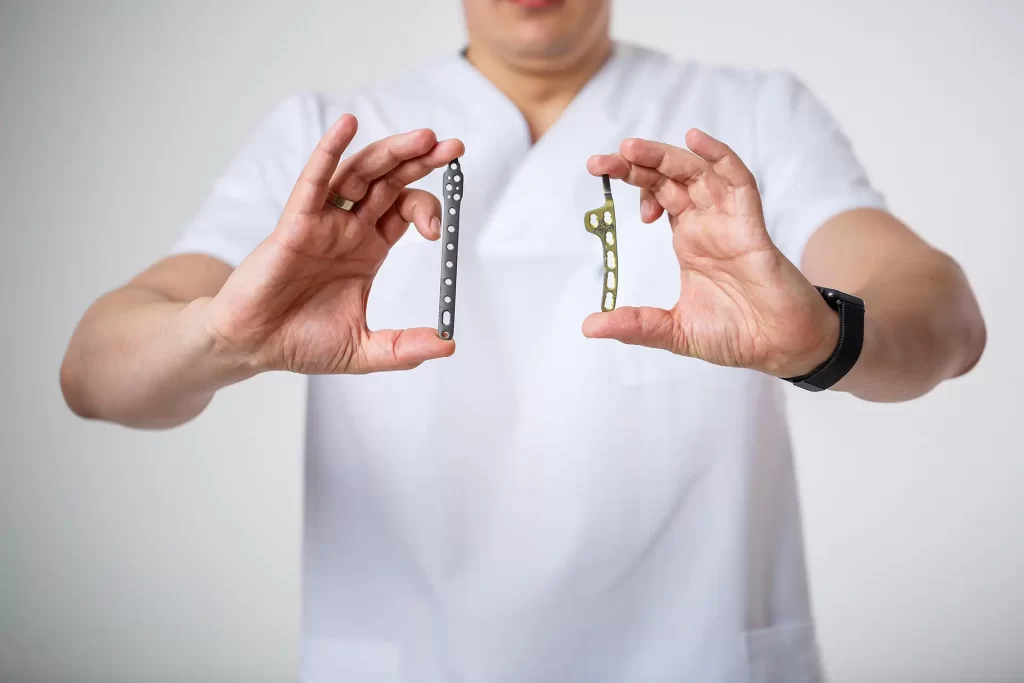
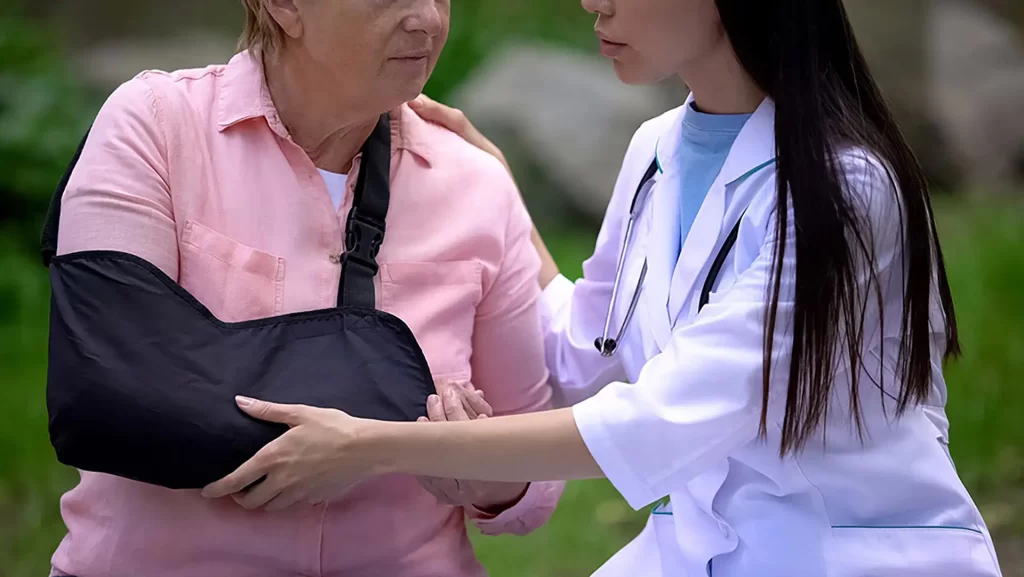
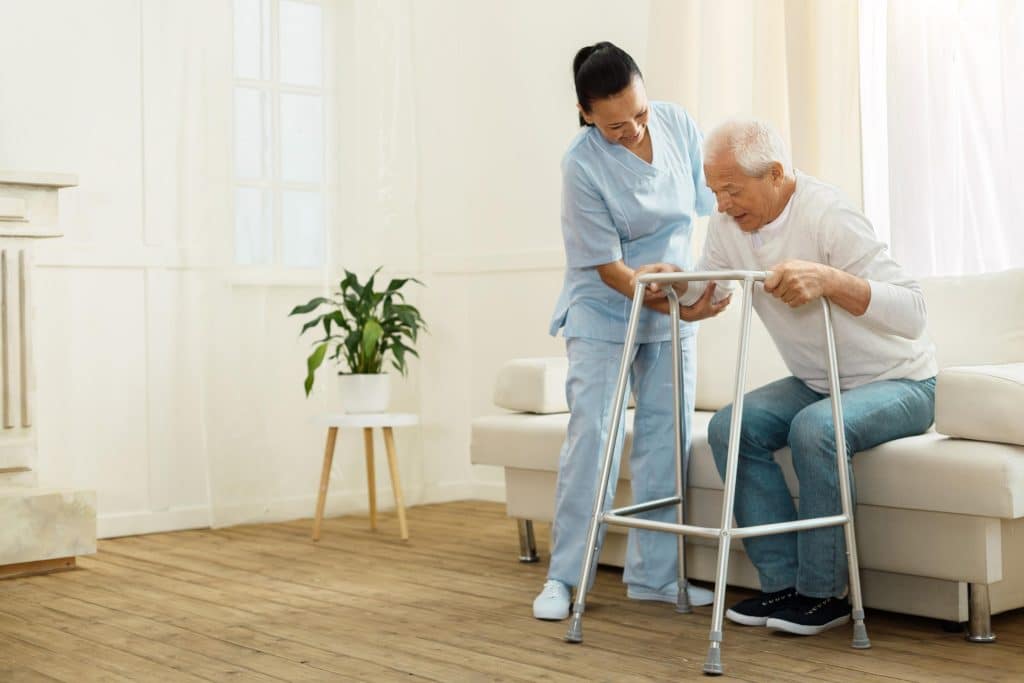
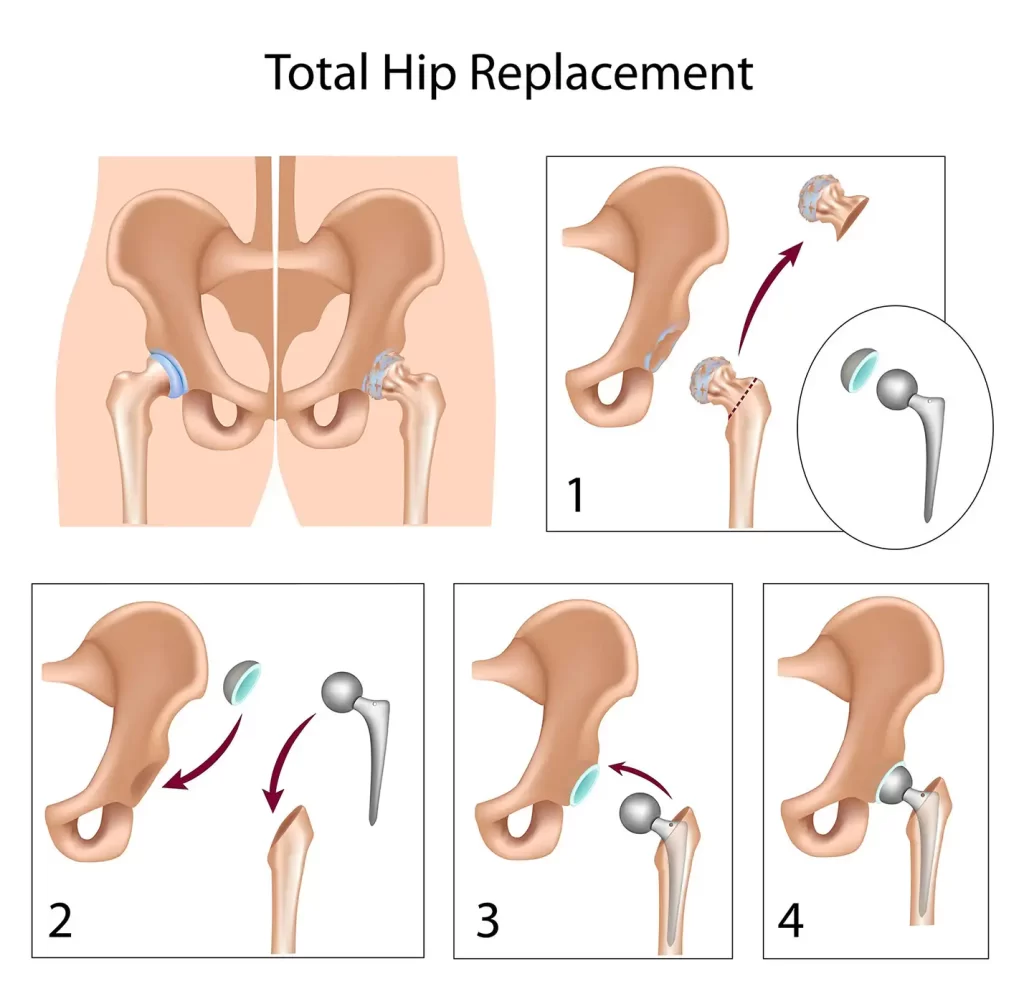
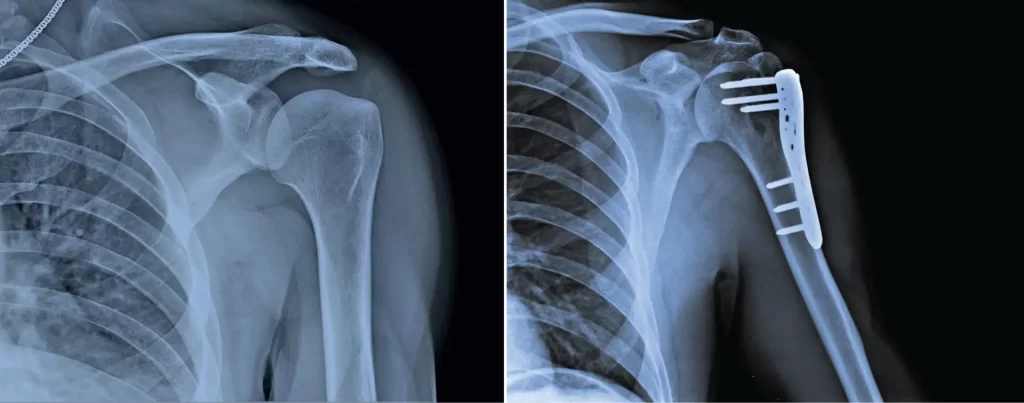
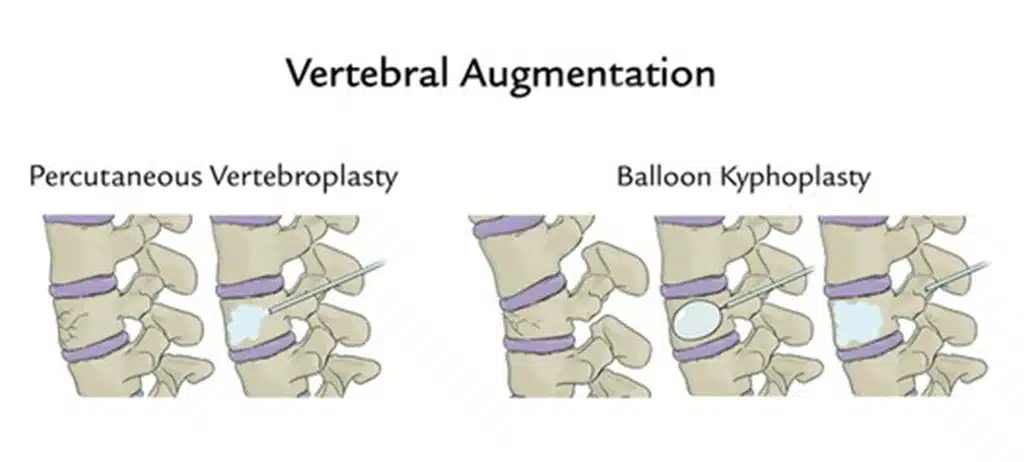
In general, treatment for geriatric fractures can be divided into conservative and surgical options, depending on the location and severity of the fracture, and how badly it affects the patient’s function and quality of life.
Conservative treatment includes painkillers, supplements (calcium, Vitamin D), physical rehabilitation as tolerated, and medications (to increase bone density) to prevent worsening of osteoporosis. Regular weight-bearing exercise and a nutritionally balanced diet are important in improving bone density and treating osteoporosis.
Below is a brief overview of how some of the more common geriatric fractures are managed, and what you can expect during these treatments.