An injured wrist and hand can be debilitating, especially since we use our hands to carry out day-to-day activities — from lighter tasks like writing to more physically strenuous tasks such as lifting objects.
We may injure our hands and wrists from overuse (chronic) or trauma (acute). Fortunately, with proper diagnosis and treatment, the injury can heal and our hands and wrists can return to normal functioning.


A wrist fracture is a medical term for a broken wrist and usually occurs from an injury such as falling down onto an outstretched hand. Severe trauma such as car accidents, motorcycle accidents or falls from a ladder cause more severe injuries. Weak bones (for example, in osteoporosis) tend to break more easily.
Common symptoms include pain and swelling, and difficulty moving the hand and wrist. Although rare, some people can still move or use the hand or wrist even if there is a broken bone. There is often pain right around the break and with finger movement. Sometimes the fingers tingle or feel numb at the tips.
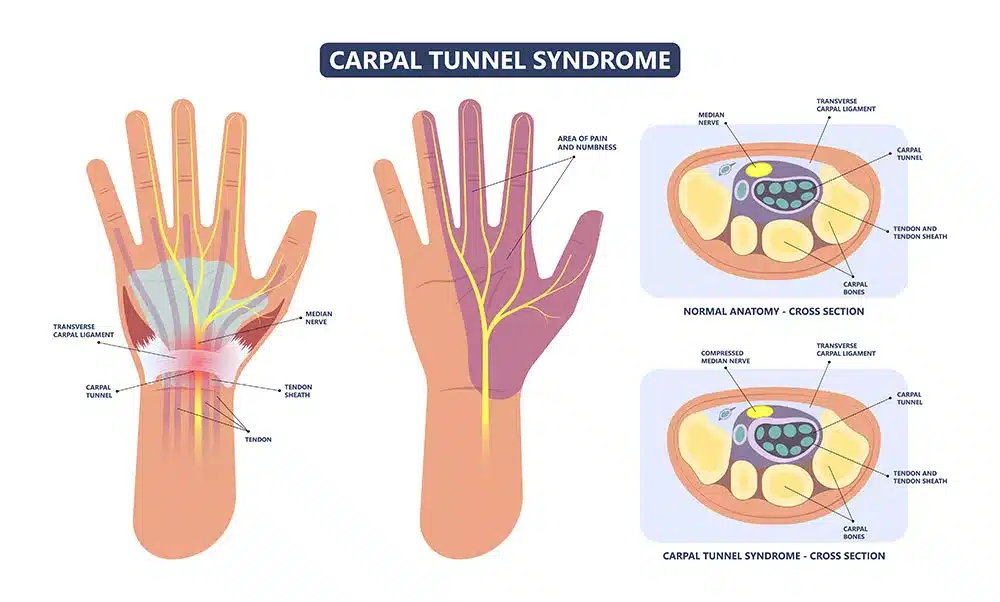
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition where the median nerve of the wrist becomes compressed. The median nerve is located at the palm-side of your hand, and it runs through a passageway called the carpal tunnel.
Common causes of carpal tunnel syndrome include wrist fractures, repetitive wrist movement (for example, using a screwdriver), and cysts in the wrist. Medical conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, and thyroid problems can also increase the risk of carpal tunnel syndrome.
Patients with carpal tunnel syndrome may experience tingling or numbness in their fingers, most commonly in the thumb, index, middle or ring fingers. Some people may also feel a sensation like an electric shock that starts in these fingers and travels up the arm. Another common symptom is weakness in the hand, making it difficult to perform everyday tasks.
Trigger finger is a condition where your finger(s) gets stuck in a bent position, as if you are pulling the “trigger”. This occurs when the tendon which attaches to your finger becomes swollen and unable to move normally.
Trigger finger is most common in people who perform repetitive and prolonged grasping movements, or frequently use their fingers forcefully (such as musicians, industrial workers). Those with osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, or diabetes are also at an increased risk of developing trigger finger.
Symptoms of trigger finger include morning finger stiffness, painful lump at the base of the affected finger, and a popping sensation when moving your finger. In severe cases, your finger may become stuck in a bent position.
De Quervain tenosynovitis is a painful condition where the tendons near the base of the thumb become inflamed. This is commonly caused by chronic overuse of the thumb and wrist. Having rheumatoid arthritis also increases your risk of developing this condition.
The main symptom of De Quervain Tenosynovitis is pain and swelling near the base of the thumb. Patients may also find it difficult to perform tasks involving grasping or pinching, and feel a “catching” sensation when moving the thumb.

Tendon, ligament and nerve injuries usually occur from trauma, such as a deep cut, sports injury, or a car accident. The symptoms you may experience will depend on the nature of the injury:
Nail bed injuries are most commonly caused by crush injuries, such as slamming your finger in a door. Nail bed injuries can cause blood to collect under your nail, a cracked nail, or your completely torn nail.
Fingertip injuries are usually caused by trauma. There are different types of fingertip injuries, such as a sharp cut, crushing injury, tearing injury, amputation, or a combination of these injuries. Fingertip injuries can damage any part of the fingertip, including the skin, soft tissue, bone, nail, and nail bed.
A finger fracture is a medical term for a broken finger. It usually occurs from an injury, such as breaking a fall with your hands or jamming your fingers when catching a ball. There is often pain, swelling, and bruising at the fracture site. Patients may also be unable to move the broken finger.
A metacarpal fracture is a medical term for a broken bone in the palm. This injury is usually a result of trauma to the hand, such as punching objects with a closed fist, or a direct blow to the hand. There is often pain, swelling, and bruising at the fracture site. Patients may also experience pain when making a fist.
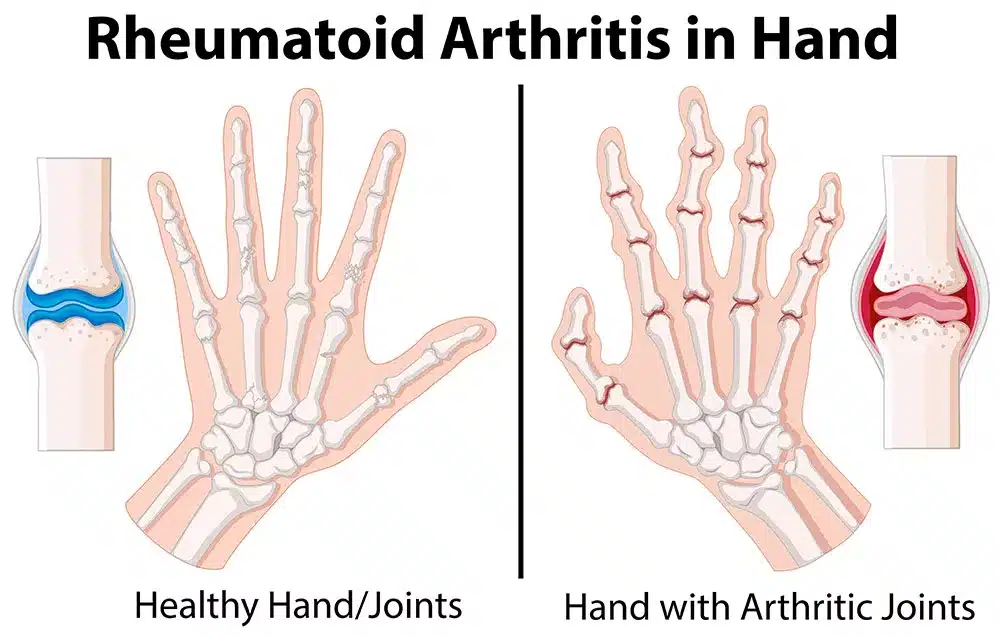
Arthritis is a condition that causes swelling and pain in your joint(s). There are two main types of arthritis: osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Osteoarthritis, also known as “wear and tear” arthritis, occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions your bones wear out. Osteoarthritis is more common in older people and those with previous hand injuries. Symptoms of hand osteoarthritis include pain and grinding when using the joint, stiffness, swelling, and weakness.
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that attacks the joints. This damages the bones, resulting in pain, swelling and morning stiffness in the joints. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis may also have a low-grade fever and get very tired.
There are many different types of lumps that can develop on the wrist or hand. The most common causes include:
If you notice a lump on your wrist or hand, be sure to see a doctor as they will be able to identify the type of lump.

Wearing wrist guards and gloves can help prevent a traumatic hand or wrist injury and taking breaks and proper posture can help prevent overuse. Sometimes, hand and wrist injuries cannot be avoided and if you do sustain one, seek immediate medical care should any of the above symptoms be present. When in doubt, consult your orthopaedist for a thorough evaluation and diagnosis.
Our friendly team is here to serve you. For urgent enquiries and appointment requests, please call or WhatsApp us directly.
